|
|
|||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
 |
|
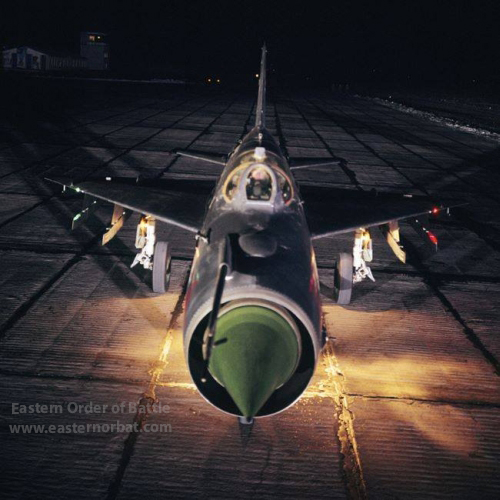
The Soviet MiG-21SM Fishbed-J tactical fighter’s |
|
Last update: 06. 02. 2022. |
|
At the turn of the sixties and seventies the MiG-21SM Fishbed-J was one of the world's best light fighters. The MiG-21SM Fishbed-J featured the new R-13-300 turbojet, a built-in GSh-23L gunpack and an improved ASP-PFD-21 gunsight. |
|
|
|
The Seventies - The first ten years: |
|
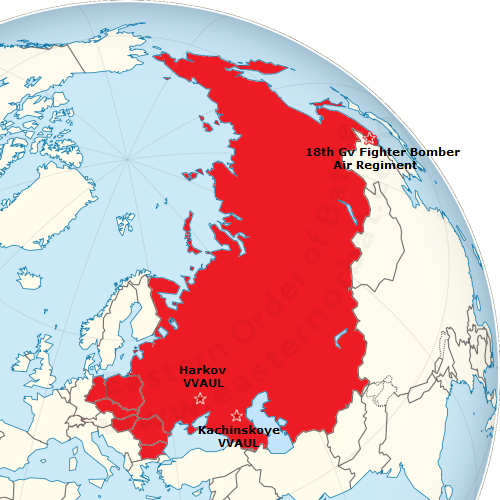
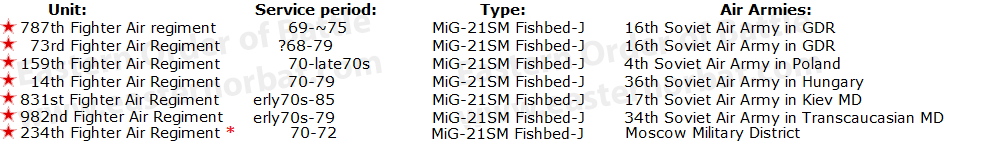
From the late sixties eight Soviet regiment received MiG-21SM Fishbed-J. Each regiment used single-seat 40 - 44 aircrafts. In the seventies, seven regiments served in Europe, one regiment in the Soviet Far East. |
 |
|
* Only one MiG-21SM Fishbed-J squadron |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
|||
|
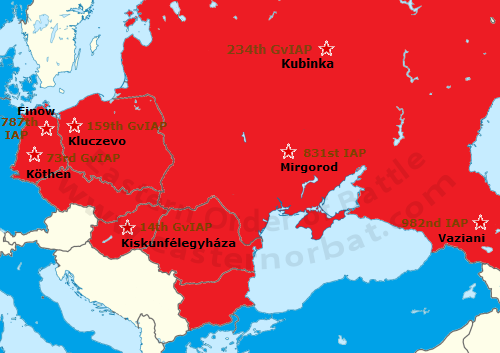
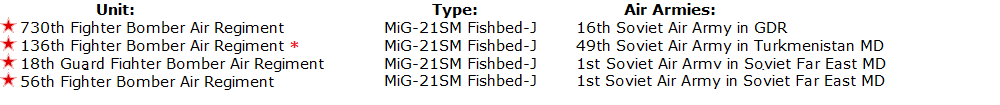
At the end of the seventies the MiG-21SM Fishbed-J fighters also received camouflage. This type was withdrawn from the first line between 1978 and 1980. Some of them were transferred to fighter-bomber air units: |
||||
 |
|
* Only two MiG-21SM Fishbed-J squadrons |
||||
|
The MiG-21SM Fishbed-J weapon systems: |
||||
|
Text source: ALEXANDER MLADENOV |
||||
|
The most important new component, incorporated into the MiG-21SM’ new mission suite, was the vastly improved RP-22S Sapfir-21 air-intercept radar, using a twist-Cassegrain antenna and featuring the monopulse target directionfinding method. This method provided notably better resistance to both passive and active jamming compared to the conical scanning, as used by the were typically detected at 30km and tracked at 15km, while against fighter-size targets the RP-22S’ maximum detection range reached 18km and tracking range was up to 11km. The RP-22S’ analogue processor calculated the minimum and maximum R-3S/R-3R launch ranges depending on the altitude and closing speed, generating the ‘launch permitted’ and ‘break’ commands. |
|
|
|
The gunsight was the new ASP-PFD-21 lead-computing gyro unit, enabling more precise firing against air targets with the GSh-23L cannon as well as generating better aiming information for using the cannon, rockets and bombs against ground and sea targets. The gunsight, however, ‘toppled’ at 2.75G, thus limiting the ability to aim the GSh-23L cannon in a high-G turning dogfight. The MiG-21SM Fishbed-J also incorporated an improved Lasour-M datalink for receiving steering commands from a ground-based intercept control station. |
|
The armament of this vastly improved Fishbed derivative was enhanced in 1974 with the addition of the R-13M AA-2C heat-seeking missile, an enhanced derivative of the R-3S AA-2A missile incorporating a modernesitive nitrogen-cooled infrared seeker and boasting better agility and extended range; it also bestowed some reduced manoeuvring limitations on the launch platform. |
 |
 |
||||
|
Weapon exhibitiony at Kupyansk airport 812th Training Air Regiment in 1990. Photo: Andrej Veskin collection |
|||||
|
The typically a combination of two R-3Ss or two R-13Ms and two R-3Rs, or two missiles on the inner pylons and two 490-litre drop tanks on the outer pylons. During the late 1970s the weapons control system of many of the MiG-21SM Fishbed-J aircraft was modified to give it the capability of firing the highly agile R-60 AAMs. |
|
The underwing pylons also received the BD3-6021D adaptor beams for carrying the MBD-2-67 multiple bomb racks and the UB-32M 32-round rocket packs. |
|
The SPS-141MVG Gvozdika is pod-mounted on the MiG-21SM fighters. Jams two distinct bands. It works in four modes: individual protection, two-aircraft protection (both aircraft having the SPS-141, cooperating with each other in jamming the enemy radar), "Doppler noise" mode, and low-level mode, where the equipment uses the terrain bounce effect in jamming. |
||
|
The Eighties - The second ten years: |
||
|
In the eighties this type was removed from the first and second-line units. The first MiG-21SM Fishbed-J arrived in 1979 to the training units. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
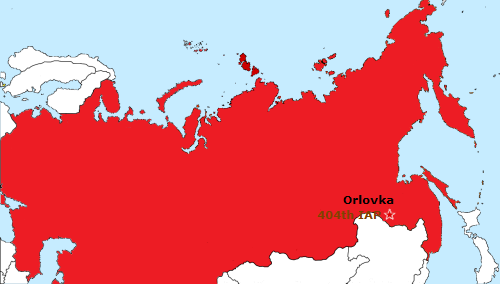
The 18th Guard Bomber Fighter Air Regiment replaced them with MiG-27D Flogger-Ds in 1989. Then after the dissolution of the Soviet Union four training regiments ceased to exist. The MiG-21SM Fishbed-J type was withdrawn in 1993. |
 |
 |
|
Tags: |